Let’s start with a basic premise that the vast majority of the world’s workloads remain in private data centers. Cloud infrastructure vendors are working hard to shift those workloads, but technology always moves a lot slower than we think. That is the lens through which many cloud companies operate.
The idea that you operate both on prem and in the cloud with multiple vendors is the whole idea behind the notion of the hybrid cloud. It’s where companies like Microsoft, IBM, Dell and Oracle are placing their bets. These died-in-the-wool enterprise companies see their large customers making a slower slog to the cloud than you would imagine, and they want to provide them with the tools and technologies to manage across both worlds, while helping them shift when they are ready.
Cloud-native computing developed in part to provide a single management fabric across on prem and cloud, freeing IT from having two sets of tools and trying somehow to bridge the gap between the two worlds.
What every cloud vendor wants
Red Hat — you know, that company that was sold to IBM for $34 billion this week — has operated in this world. While most people think of the company as the one responsible for bringing Linux to the enterprise, over the last several years, it has been helping customers manage this transition and build applications that could live partly on prem and partly in the cloud.
As an example, it has built OpenShift, its version of Kubernetes. As CEO Jim Whitehurst told me last year, “Our hottest product is OpenShift. People talk about containers and they forget it’s a feature of Linux,” he said. That is an operating system that Red Hat knows a thing or two about.
With Red Hat in the fold, IBM can contend that being open source; they can build modern applications on top of open source tools and run them on IBM’s cloud or any of their competitors, a real hybrid approach.
Microsoft has a huge advantage here, of course, because it has a massive presence in the enterprise already. Many companies out there could be described as Microsoft shops, and for those companies moving from on prem Microsoft to cloud Microsoft represents a less daunting challenge than starting from scratch.
Oracle brings similar value with its core database products. Companies using Oracle databases — just about everyone — might find it easier to move that valuable data to Oracle’s cloud, although the numbers don’t suggest that’s necessarily happening (and Oracle has stopped breaking out its cloud revenue).
Dell, which spent $67 billion for EMC, making the Red Hat purchase pale by comparison, has been trying to pull together a hybrid solution by combining VMware, Pivotal and Dell/EMC hardware.
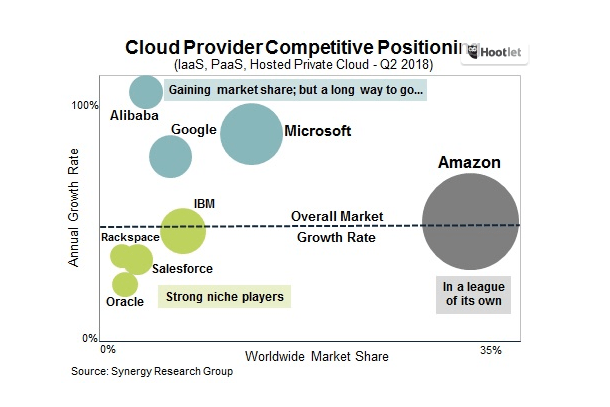
Cloud vendors reporting
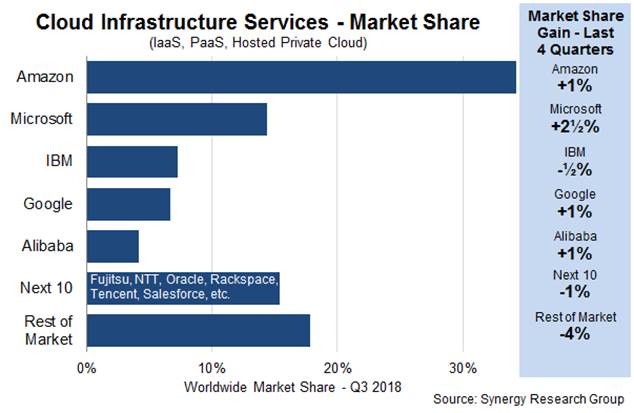
You could argue that hybrid is a temporary state, that at some point, the vast majority of workloads will eventually be running in the cloud and the hybrid business as we know it today will continually shrink over time. We are certainly seeing cloud infrastructure revenue skyrocketing with no signs of slowing down as more workloads move to the cloud.
In their latest earnings reports, those who break out such things, the successful ones, reported growth in their cloud business. It’s important to note that these companies define cloud revenue in different ways, but you can see the trend is definitely up:
- AWS reported revenue of $6.7 billion in revenue for the quarter, up from $4.58 billion the previous year.
- Microsoft Intelligent Cloud, which incorporates things like Azure and server products and enterprise services, was at $8.6 billion, up from $6.9 billion.
- IBM Technology Services and Cloud Platforms, which includes infrastructure services, technical support services and integration software reported revenue of $8.6 billion, up from $8.5 billion the previous year.
- Others like Oracle and Google didn’t break out their cloud revenue.
Show me the money
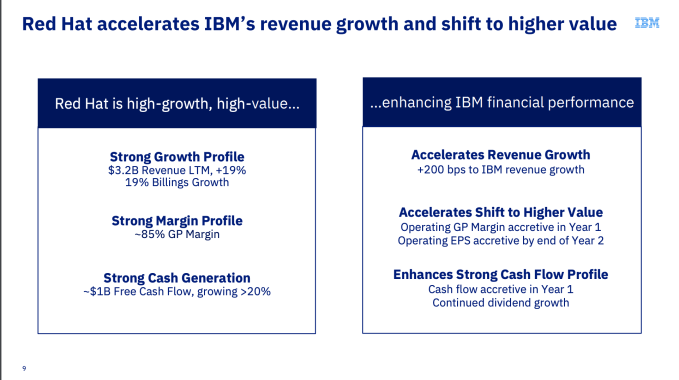
All of this is to say, there is a lot of money on the table here and companies are moving more workloads at an increasingly rapid pace. You might also have noticed that IBM’s growth is flat compared to the others. Yesterday in a call with analysts and press, IBM CEO Ginni Rometty projected that revenue for the hybrid cloud (however you define that) could reach $1 trillion by 2020. Whether that number is exaggerated or not, there is clearly a significant amount of business here, and IBM might see it as a way out of its revenue problems, especially if they can leverage consulting/services along with it.
There is probably so much business that there is room for more than one winner, but if you asked before Sunday if IBM had a shot in this mix against its formidable competitors, especially those born in the cloud like AWS and Google, most probably wouldn’t have given them much chance.
When Red Hat eventually joins forces with IBM, it at least gives their sales teams a compelling argument, one that could get them into the conversation — and that is probably why they were willing to spend so much money to get it. It puts them back in the game, and after years of struggling, that is something. And in the process, it has stirred up the hybrid cloud market in a way we didn’t see coming last week before this deal.









 So to meet that opportunity, the team decided to raise a new round to scale out both its team and product. And now, that product includes a commercial offering of Pulumi with the company’s new ‘team edition.’ This new enterprise version includes support for unlimited users, integrations with third-party tools like GitHub and Slack, as well as role-based access controls and onboarding and 12×5 support. Like the free, single-user community edition, the team edition is delivered as a SaaS product and supports deployments to all of the major public and private cloud platforms.
So to meet that opportunity, the team decided to raise a new round to scale out both its team and product. And now, that product includes a commercial offering of Pulumi with the company’s new ‘team edition.’ This new enterprise version includes support for unlimited users, integrations with third-party tools like GitHub and Slack, as well as role-based access controls and onboarding and 12×5 support. Like the free, single-user community edition, the team edition is delivered as a SaaS product and supports deployments to all of the major public and private cloud platforms.